Which of the Following Has the Second Largest Ionization Energy
The entropy equals GT P and hence a constant entropy corresponds to a constant slope of the line representing the dependence of the free energy G on temperature T. For example a 5000-V potential difference produces 5000-eV electrons.

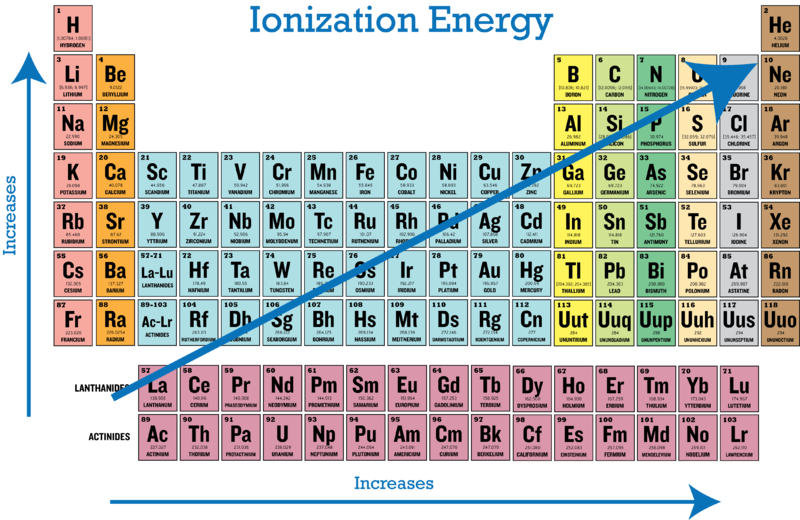
The Parts Of The Periodic Table
The second element of the following group.

. This is so low that when it undergoes isomeric transition the emitted gamma radiation is in the ultraviolet range. In general this assumption is not representative of the real behavior. Thorium has three known nuclear isomers or metastable states 216m1 Th 216m2 Th and 229m Th.
The energy of the electron in electron-volts is numerically the same as the voltage between the plates. The entropy of a phase. The conceptual construct namely two parallel plates with a hole in one is shown in a while a real.
By conservation of energy the kinetic energy has to equal the change in potential energy so K E q V K E q V. This type of diagonal similarity is commonly referred to as diagonal relationship in the periodic table. Thus lithium shows similarities to magnesium and beryllium to aluminium in many of their properties.
Note that the standard free energy change for the reaction is for the changes from the reactants in their standard states to the products in their standard states. The diagonal relationship is due to the similarity in ionic sizes and or chargeradius ratio of the elements. On the second ionization of the same acid there are now three ions and the anion has a charge so the entropy again decreases.
As shown there the energy and entropy of each phase has been assumed to be independent of temperature ie. Of the following elements which one would have the largest first ionization energy. 229m Th has the lowest known excitation energy of any isomer measured to be 76 05 eV.

File Ionization Energy Periodic Table Svg Wikipedia
Comments
Post a Comment